The World Health Organization defines Sexual Health as a state of physical, emotional, mental and social well-being related to sexuality; it is not merely the absence of disease, dysfunction or infirmity. Sexual health requires a positive and respectful approach to sexuality and sexual relationships, as well as the possibility of having pleasurable and safe sexual experiences, free of coercion, discrimination and violence. For sexual health to be attained and maintained, the sexual rights of all individuals must be respected, protected and fulfilled.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) and Sexually Transmitted Infections (STDs) are common conditions transmitted through sex-related activities.


While it’s a topic that can be uncomfortable for some to talk about, it is incredibly important to learn about.
There are many ways to reduce your chances of contracting an STI, but as long as you engage in any sexual activity at all, there is still a risk.


Therefore aside from practicing safe sex, the key to reducing your chances of spreading an STI, or experiencing complications further down the line, is knowing what symptoms to look out for and the best way to communicate about STIs to protect yourself and your partners.
There are many ways to reduce your chances of contracting an STI, but as long as you engage in any sexual activity at all, there is still a risk.

Symptoms of STIs

Many STIs carry no symptoms, or ones that aren’t easily noticeable. Therefore, if you are or have been sexually active, it is important to see a healthcare professional for any of the symptoms below to be sure.
STI Symptoms in Men
Thick green or yellow discharge from the penis or bottom, Urethra (Penis) irritation, Pain and swelling in testicles, Warts around penis and anus, Small blisters that burst to leave red, open sores around your genitals, anus, thighs or bottom – the sores may be less red on brown or black skin, Tingling, burning or itching around your genitals. Pain when you pass urine, Discharge that is not usual for you, Itching usually worse at night, Small red or blue spots on your skin, White/yellow dots attached to your hair, Dark red or brown spots in your underwear, Crusted or sticky eyelashes, if they are affected, Sores, bumps, lumps or spots on or in genitals, oral area or rectal area, Itching, tingling or burning around genitals, Burning or painful sensation when urinating, Pain during sex, Pain in the lower abdomen, Rash on hands or feet, Fever, White dots or black powder in underwear.

STI Symptoms in Women

Unusual Thick green or yellow vaginal discharge, Vaginal discharge with a strong smell, Unusual bleeding between periods, Bleeding after sex, Pain in tummy, on passing urine, Warts around vagina and anus, Small blisters that burst to leave red, open sores around your genitals, anus, thighs or bottom – the sores may be less red on brown or black skin, Tingling, burning or itching around your genitals, Pain when you pee, Discharge that is not usual for you, Sores, bumps, lumps or spots on or in genitals, oral area or rectal area, Itching, tingling or burning around genitals, Burning or painful sensation when urinating, Pain during sex, Pain in the lower abdomen, Rash on hands or feet, Fever, White dots or black powder in underwear.
Common Types of STIs
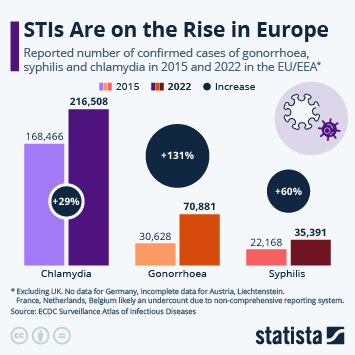
There are over 30 types of known sexually transmitted diseases or infections. While there is a long list of sexually transmitted infections, there are a few that are incredibly common and therefore both most easily spread and most commonly tested for. Some of these are included below.

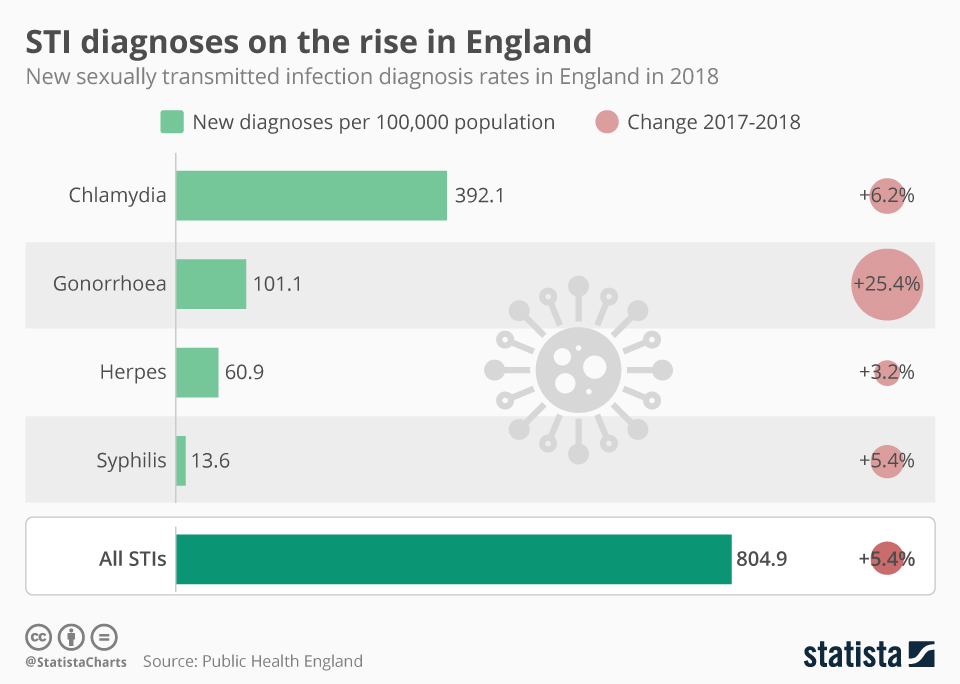
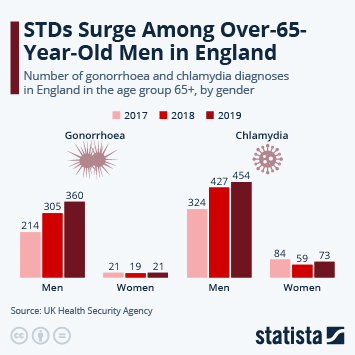
Chlamydia Infection is one the most common sexually transmitted Infections (STIs). You can get chlamydia from intercourse, anal sex, or oral sex. Because this infection does not cause symptoms, many people who have this infection do not know it and unknowingly infect other people. Regular screening can help reduce spread of this infection.
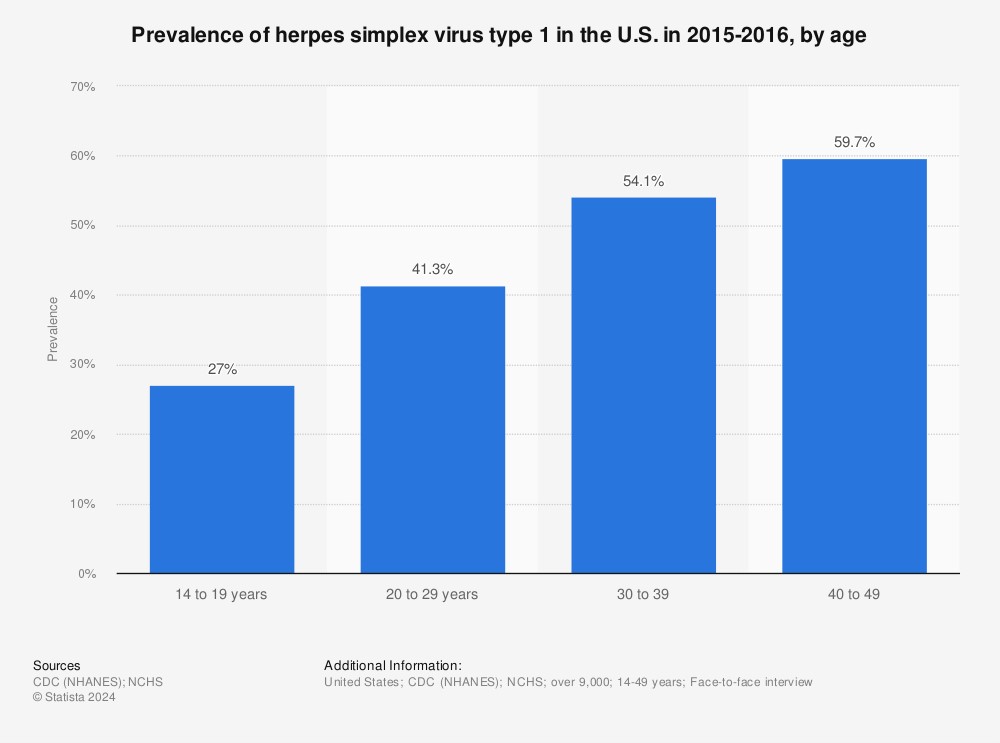
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) causes oral herpes, genital herpes and infections in other areas of your body. Fluid filled blisters on your skin are common symptoms, but many people have no symptoms at all. A simple blood test can tell you if you have HSV in your body.
Genital warts are the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI). Certain types of HPV cause genital warts. These types don’t cause cancer. Treatments can get rid of genital warts, but once you have genital warts and HPV, you can always give the STI to someone else. It’s important to use condoms and practice safe sex.
Gonorrhea, or “the clap,” is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). Often, gonorrhea doesn’t cause symptoms, especially in people assigned female at birth. When present, symptoms differ based on your reproductive parts. See your healthcare provider if you think you’re infected. Prompt treatment with antibiotics can prevent long-term problems.
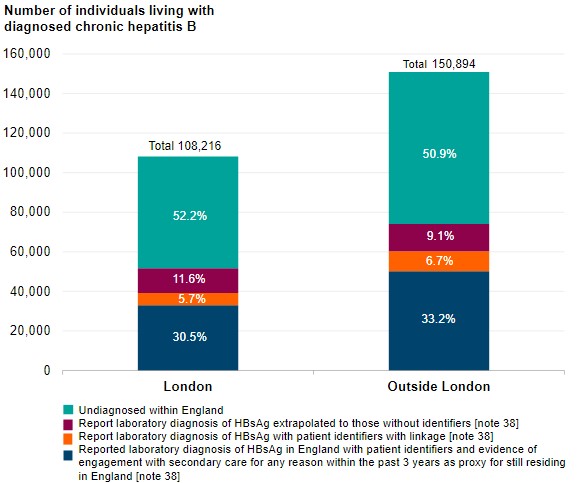
Hepatitis B is one of five viruses that can infect your liver, causing inflammation. It’s spread through bodily fluids. Most people only have a brief, acute infection. But for some people, it becomes chronic. A chronic infection can do serious long-term damage to your liver. Hepatitis B is preventable with a vaccine, but it has no cure.
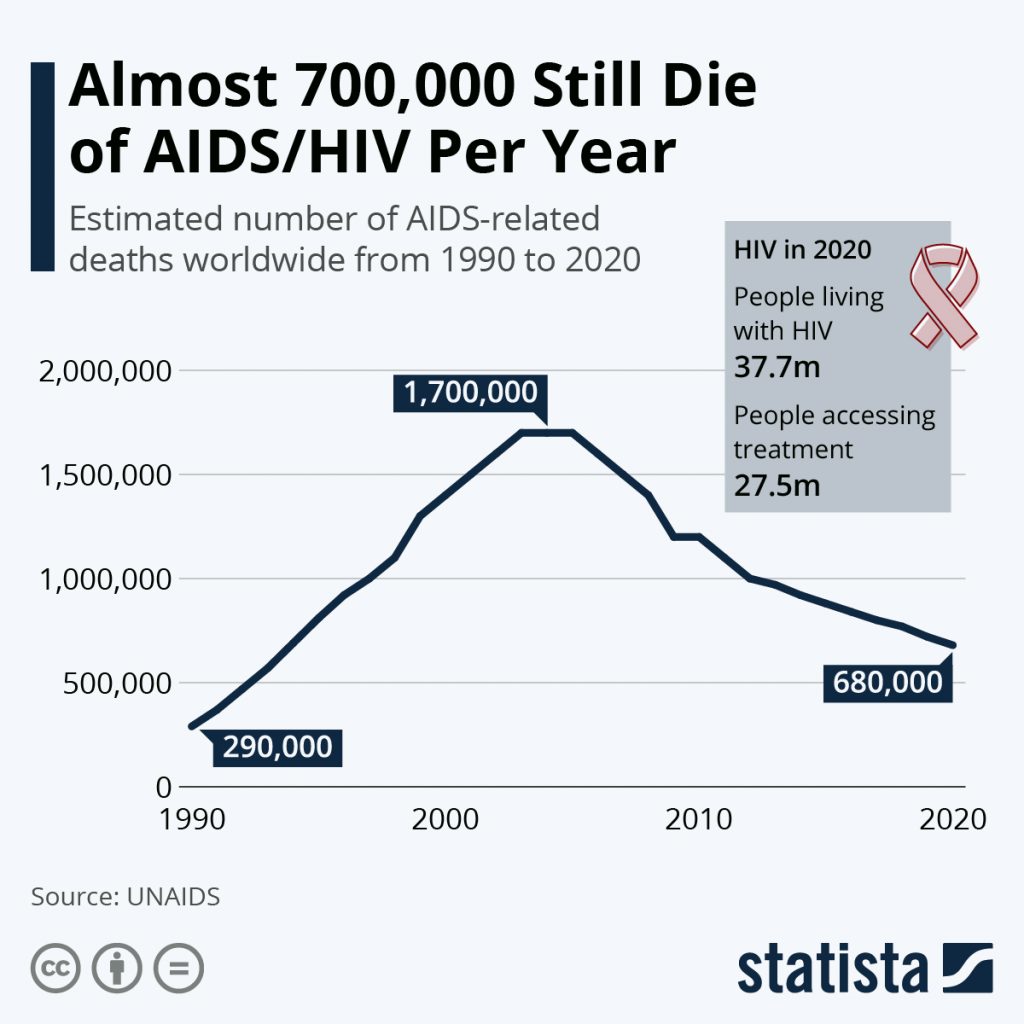
Human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). HIV weakens your immune system by destroying your special cells called T-cells until you are able to fight off even minor illnesses. You can have HIV without any symptoms. Getting tested and starting treatment early gives you the best chance of living a long life.
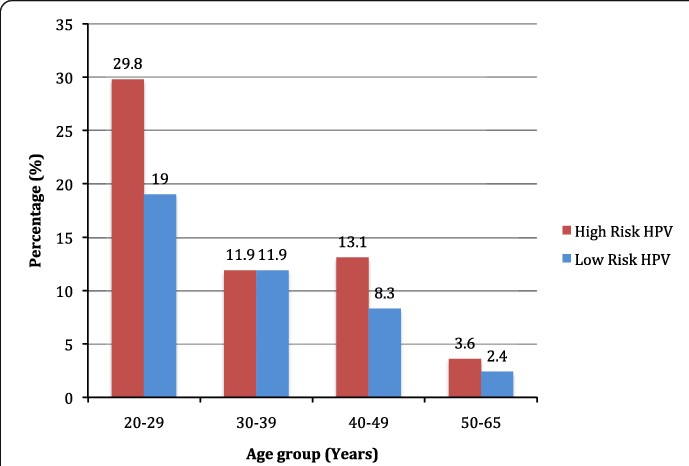
More than 30 strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV) can affect your genitals. These include harmless forms of HPV, like those that cause genital warts. Only some types of HPV are considered “high risk” because they can progress to cervical cancer. Getting vaccinated against HPV and receiving regular Pap smears can prevent cervical cancer.
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that’s treatable with medication. Without treatment, syphilis causes serious health problems. It can permanently damage your heart, brain, muscles, bones and eyes. To reduce your risk of infection, always use a condom during sex.
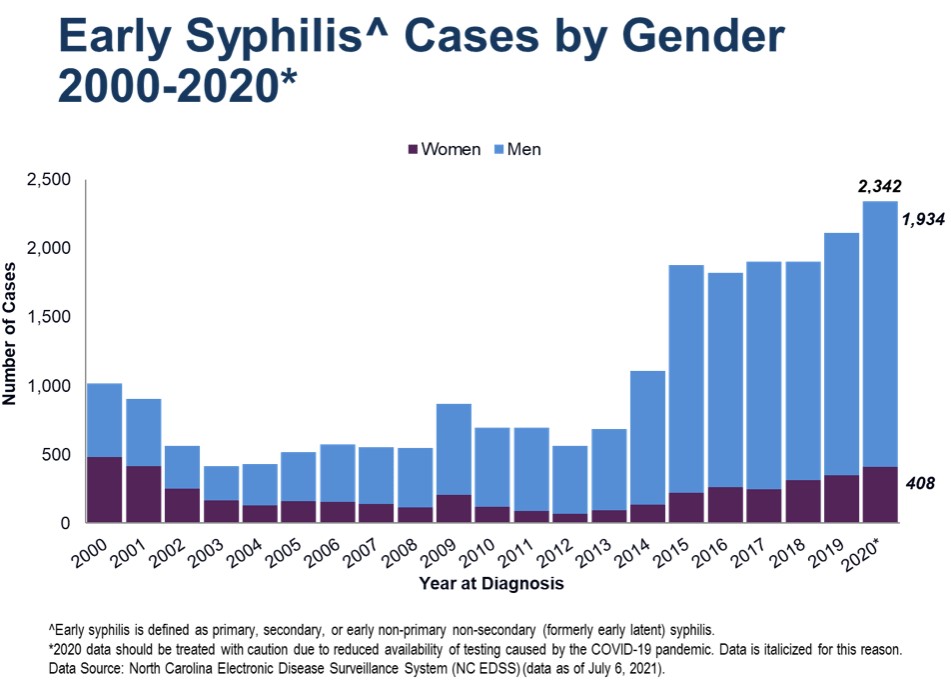
Risk Factors

Being sexually active carries the risk of being exposed to an STI or STD, but there are some factors that make it more likely. These include, Having unprotected sex – other types of sex is less risky than penetrative sex but still carries risk, Having sexual contact with several partners – the risk of exposure to an STI increases with the number of people you have sexual contact with, Having previously had an STI – having an STI makes it easier to get infected, Misuse of alcohol or drugs – reduction in judgement has been linked to a higher risk of participating in an activity that may result in an infection.
Complications
In many cases, STIs and STDs go undetected for a long period of time, as there are commonly no symptoms in the early stages. Because of this, there are cases that a diagnosis comes later due to complications of the infection. These can include, Pregnancy complications, Infertility, Cancer, Pelvic pain, Pelvic inflammatory disease, Heart disease.

Other Infections
Pain During or After Sex
Dyspareunia or pain during or after sexual intercourse can occur both in men and women but is more common among women. Male dyspareunia or dyspareunia in men is a recurrent or continuous pain in the genital or pelvic region which occurs during or after sexual activity. The pain in the penis may be accompanied by a burning sensation during and even after ejaculation.

Burning / Pain on Passing Urine after Sex
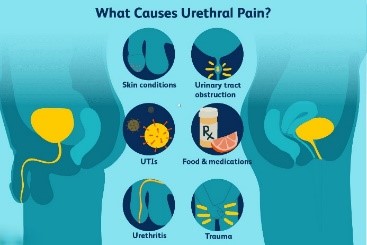
Burning / Pain on Passing Urine after Sex is the most commonly reported symptom. Pain can occur at the start of passing urine or after passing urine. Pain at the start of passing urine is often a symptom of a urinary tract infection. Pain after passing can be a sign of a problem with the urinary bladder in any of the genders or prostate in men.
Irritation of Testes or Penis
Many different infections such as fungal infection psoriasis or some sexually transmitted infections can cause genital irritation / penis or testes irritation. Genital Irritation / penis or testes irritation can also come from contact with household products like soap or latex condoms.
Itching of Testes or Penis

Genital Itching or Itching of the Penis or Testes in a man’s private parts can be a symptom of many different conditions, including jock itch, eczema or sexually transmitted infections. While the itching may go away with simple measures, treatment and medication may be needed in some cases.
Pain in Testes or Penis
Some common causes of Genital Pain / pain in Penis or Testes or pelvic pain among men include sexual intercourse, enlarged prostate and hernias. Less common causes include testicular torsion and certain kinds of cancer. See a healthcare provider any time you have new pelvic pain.

Ulcers on Testes or Penis

People usually seek healthcare at the final stage of the painful Genital Ulcer / ulcer of the Penis or Testes. Among men, the ulcers are usually on the penis (foreskin, shaft and sometimes on the glans (the cap like part), and as many as 50% develop unilateral or bilateral painful swellings.
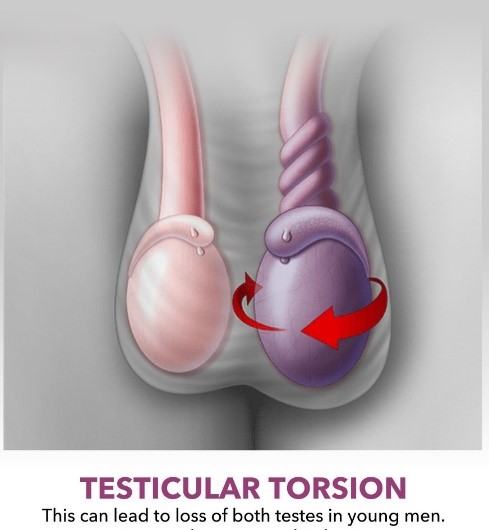
Twisting of the Testes Apparatus
Twisting of the Testes or Testicular torsion is an emergency condition. It happens when the spermatic cord, which provides blood flow to the testis, rotates and become twisted. The twisting cuts off the testis blood supply and causes sudden pain and swelling. This condition can also cause infertility in men.
Urine Drops / Uncontrolled Urine Problem

Urinary Incontinence / Urine Drops / Uncontrolled Urine / Urinary Incontinence, the loss of bladder control is a common and often embarrassing problem. The severity ranges from occasionally leaking urine when you cough or sneeze to having an urge to urinate that’s so sudden and strong you don’t get to a toilet in time.
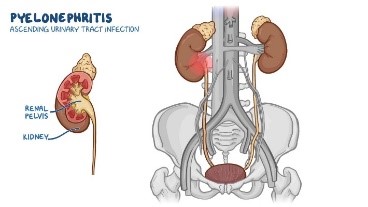
Infection of the Kidneys
Pyelonephritis or this infection of the kidneys is most often a result of an infection that has spread up the urinary tract, or from a blockage in the urinary tract. A blockage causes urine to back up into the ureters and kidneys.
Infection of the Prostate
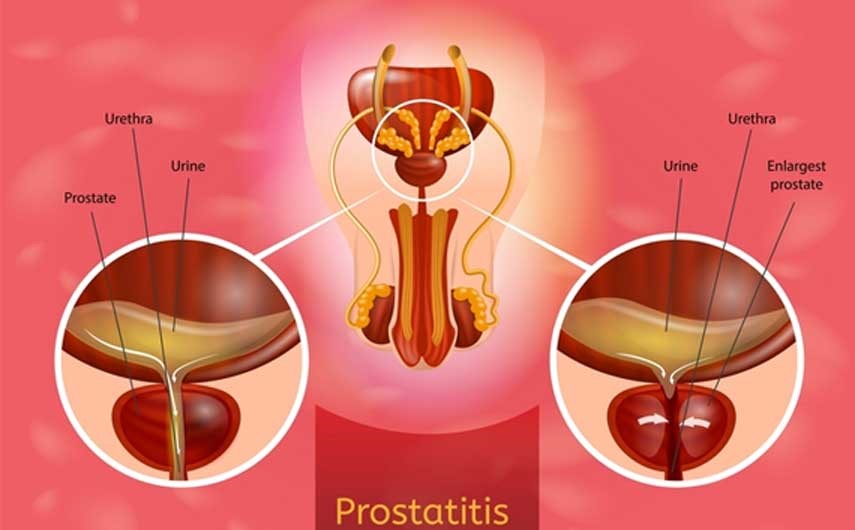
Prostatitis or infection of the Prostate is a group of conditions that includes acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome. It can cause infection, inflammation and pain in the prostate gland. In this disease there is frequent episodic and sometimes continuous discharge from the Penis.
Infection of the Urinary Bladder
Cystitis is the infection of the lower urinary tract, or more specifically, the urinary bladder. It may be broadly categorized as either uncomplicated or complicated. Uncomplicated cystitis refers to lower urinary tract infection in either men or non- pregnant women who are otherwise healthy.
Infection of the Urethra, the Penis
Urethritis is the infection of the urethra (tube like structure inside the Penis), that carries urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body. This tube becomes swollen and sores develop. It is often caused by sexually transmitted infection. It is important to get treated to avoid it spreading.
Infection of the Epididymis
Epididymitis is the inflammation of the coiled tube called Epididymis, responsible for transport of sperm. The infection may cause fertility problems in men.
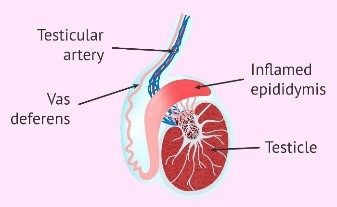
Infection of the Seminal Vesicles
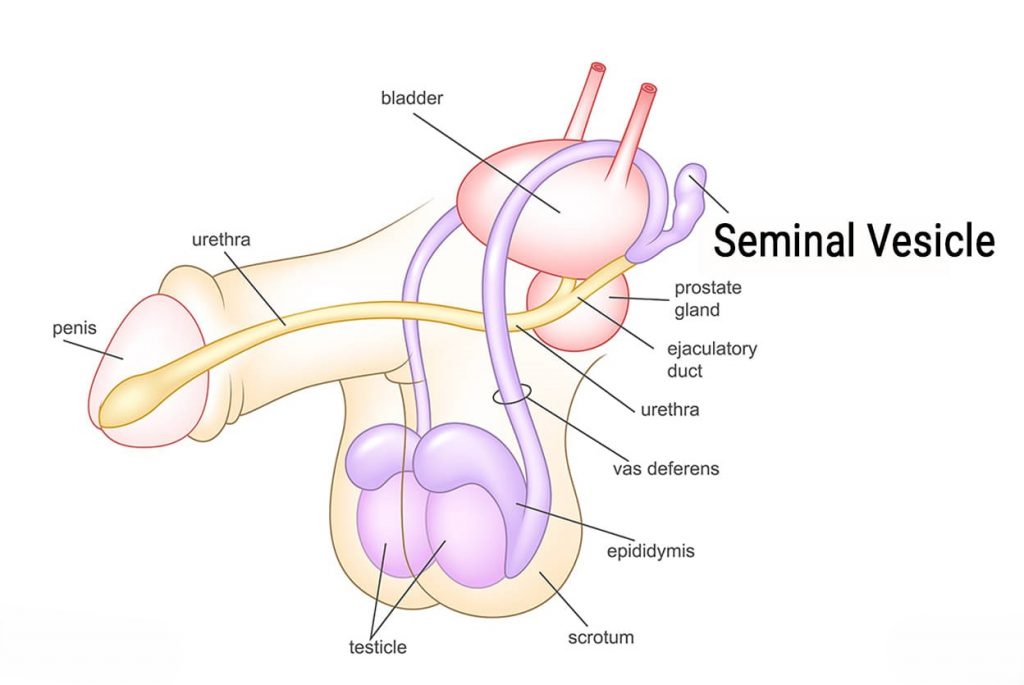
It is inflammation of seminal vesicles. Seminal vesicles are the part of the reproductive system in men responsible for fertility.
Infection of the Testes
Orchitis is inflammation of one or both testes. Bacterial, Viral or sexually transmitted infections can cause Orchitis. The infection can lead to fertility problems in men.