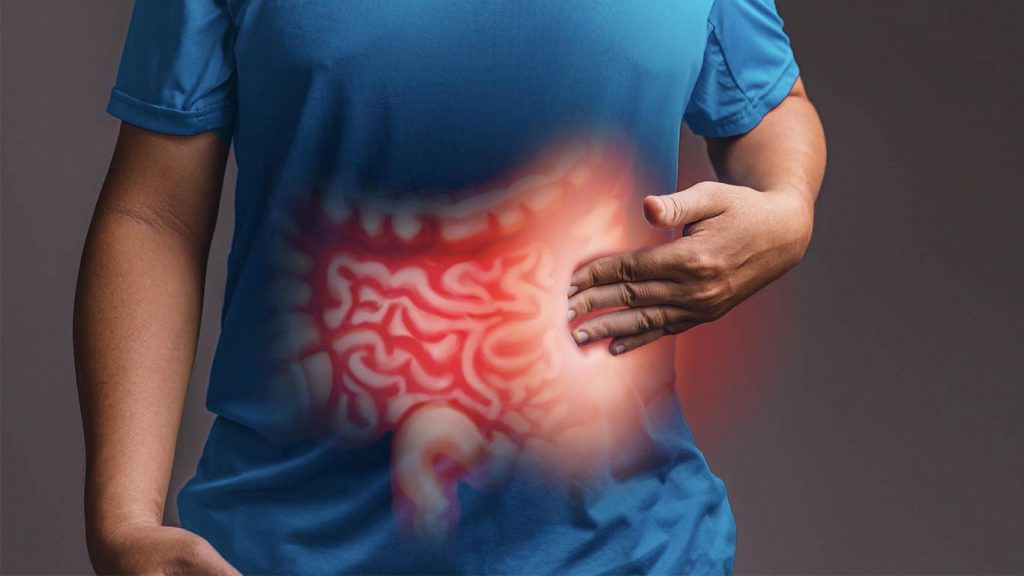
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a term for two conditions (Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis) that are characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Prolonged inflammation results in damage to the GI tract.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a term that describes disorders involving long-standing (chronic) inflammation of tissues in your digestive tract. Types of IBD include:
- Ulcerative colitis. This condition involves inflammation and sores (ulcers) along the lining of your large intestine (colon) and rectum.
- Crohn’s disease. This type of IBD is characterized by inflammation of the lining of your digestive tract, which often can involve the deeper layers of the digestive tract. Crohn’s disease most commonly affects the small intestine. However, it can also affect the large intestine and uncommonly, the upper gastrointestinal tract.
- Both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease usually are characterized by diarrhea, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, fatigue and weight loss.
- For some people, IBD is only a mild illness. For others, it’s a debilitating condition that can lead to life-threatening complications.